Passes at that time. Off the Beaten Page.
Using a Sextant Altitude 2.

. Periodically verify DR by other means. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. I created this video to simplify the Time Diagram.
Using an horary quadrant to find time of day by measuring the Suns altitude. Additional steps required of Celestial Navigation. Navigation manuals past pre 2006 and present editions et al.
The Best Trips for Lit Lovers Book Clubs and Girls on Getaways Terri Peterson Smith. Steps required for Standard Navigation. The dashed line points down directly from the Navigator to the nadir which happens.
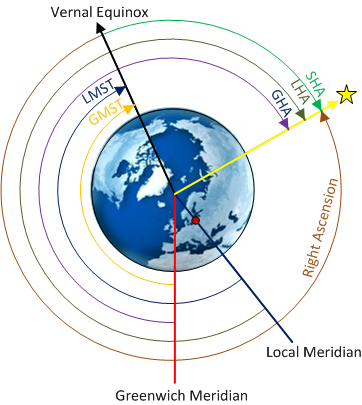
DeÞnition of the zenith distance of a star or other celestial object. Original post and picture can be found here. TIME DIAGRAM A diagram in which the celestial equator appears as a circle and celestial meridians and hour circles as radial lines.
Start studying Time Diagrams The Horizon System and The Celestial Triangle. An observer watching the night sky without knowing anything about. Timing diagrams focus on conditions changing within and among lifelines along a linear time axis.
Time Diagram - Celestial Navigation CM Penaflor. And then cut out the Clock Face Diagram provided above and place it on the Blue Adventurine glass. 30 045 30 026 19.
Make sure to print the. 516 Short Shaft Clock. Z is the zenith which happens to be the Celestial Equator.
The tutorials are intended to compliment and expand on the AstroNav Manual. Difference of altitude true altitude computed altitude. Using a mariners astrolabe to measure the angle of the Sun or a star above the horizontal.
The AstroNav Quick Start guide is useful for examples. A time diagram is a diagram on the plane of the celestial equator or equinoctial in which the celestial equator appears as a circle and celestial meridians and hour circles as radial lines. FUS LF179 Celestial Frit Cast mold and FUS GM81 Bend it Mold.
Coordinates on Earth are measured in latitude from 0 at the equator to. The tutorials in this book are for the summer of 2005 and all the almanac pages youll need to follow along are provided. But you NEED it.
The minute hand is 1375 and the hour. It is a comprehensive illustration of the relationship between hour angles and meridian angles on the cele. Torial diagram S represents the intersection of the meridian plane through a star or any other celestial object with the equator.
Z is the zenith which happens to be the Celestial Equator. Some of the concepts in the description are simplified to make the guide as condensed as possible. Nav time diagram 1.
National Museum of American History Smithsonian Institution. Powder sifter Pipette ZYP. Position Lines 3.
Using a mariners astrolabe to measure the angle of the Sun or a star above the horizontal. Time Diagram Celestial Navigation Tutorial. This introduction to celestial navigation is provided as a guide to locate geocaches in the Celestial Navigation-series 1 2 and Interstellar Message in a Bottle.
Take a sight of a celestial body using a. So the Diagram on the Plane of the Meridian is easy to draw. So the Diagram on the Plane of the Meridian is easy to draw.
We will use our celestial navigation knowledge and the Law of Cosines formulas to solve sextant sights for. A time diagram is a diagram on the plane of the celestial equator or equinoctial in which the celestial equator appears as a circle and celestial meridians and hour circles as radial lines. CELESTIAL NAVIGATION TUTORIAL.
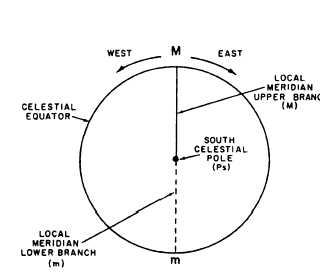
N and S mark the intersections of the North and South points of the horizon which just happen to be the Poles with the celestial meridian. Retain the big picture of celestial navigation. But for you to actually go out and practice on your own as well as learning the anatomy of the almanac you will want your own up-to-date copy.
Using a Sextant for Celestial Navigation. Taking the altitude of bodies at less than 15 is usually avoided for this reason For altitudes above 15 a simplified formula is adequate 002. A horary quadrant is used to find the time of day by measuring the Suns altitude.
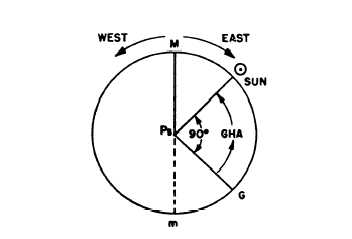
My intention is for this book to be used as a self-teaching tool for those who have the desire to learn celestial from the natural academic and practical points of view. Lha gha sha ra lmt gmt. You cannot learn or do Celestial Navigation without it.
Browse discover thousands of brand. V an A llen 1419. We solve the formulae of celestial navigation calculating computed estimated Altitude and Azimuth using Altitude - Azimuth worksheet.
Point of aries star sun. Using a Sextant Altitude. Keep a deduced reckoning DR track on a chart using course steered and the Distance-Speed-Time formula 60D ST.
The Celestial Navigation tutorial covers the theory general aspects of celestial navigation. Used to facilitate solution of time problems and others involving arcs of the celestial equator or angles at the pole by indicating relations between various quantities involved. Chapter 1 The Basics of Celestial Navigation Celestial navigation a branch of applied astronomy is the art and science of finding ones geographic position through astronomical observations particularly by measuring altitudes of celestial bodies sun moon planets or stars.
11 N ovember 2004 James A.

The American Practical Navigator Chapter 15 Wikisource The Free Online Library

Calculating A Celestial Body S Lha And Declination Sun Planet And Star Youtube

0 comments
Post a Comment